Herniated Disc Treatment, If you are one of the millions of people suffering from the pain and discomfort of a herniated disc, you don’t have to suffer in silence any longer. We know that life with a herniated disc can be difficult, but there are treatments available that can help you manage your pain and get you back to living a full and active life. This blog post will discuss the basics of herniated disc treatment and explore the various options available to help you say goodbye to pain and discomfort. We’ll also provide tips to help you manage your herniated disc, so you can get back to living your best life.
So whether you’re looking for relief from your herniated disc or just curious about the treatment options available, this blog post is for you. Read on to learn more about herniated disc treatment and how to say goodbye to pain and discomfort!
Definition of the herniated disc
A herniated disc is a medical condition that results when the soft tissues that cushion the spinal cord between the vertebrae (bones) protrude and press on the spinal cord itself. This can cause pain and decreased mobility in the lower back and neck. In some cases, the herniated disc can rupture, which can lead to serious spinal cord damage.
Different Types of Herniated Disc
There are many different types of herniated discs, but the most common is disc herniation syndrome. This is when a disc in the spine becomes bulging and Starts to protrude from the spinal canal. This can cause a lot of pain and discomfort and can lead to nerve damage if not treated quickly. If the herniated disc is not treated, it can eventually cause complete paralysis.
Cervical Disc Herniation
Cervical disc herniation is a condition in which the cervical disc bulges out from the vertebral column. This herniation can cause neck pain and difficulty breathing. Cervical disc herniation is most common in women over the age of 50, but it can also occur in younger women. The cause of cervical disc herniation is unknown, but it may be caused by a number of factors, including age, injury, or genetics. Treatment for cervical disc herniation depends on the severity of the herniation and the patient’s symptoms. If the herniation is mild, treatment may include pain relief and physical therapy. If the herniation is more severe, surgery may be necessary to remove the disc.
Thoracic Disc Herniation
Thoracic disc herniation is a condition in which the thoracic disc bulges out of its normal location. This can cause pain and disability. Thoracic disc herniation is most common in people over the age of 50. It can also occur in people who have had a previous herniation, as well as in people who have a condition that affects the discs in the spine.
Lumbar Disc Herniation
Lumbar disc herniation is a debilitating medical condition in which the intervertebral disc between the lower back and the pelvis herniates, or protrudes out of its space. This can cause severe pain in the lower back and legs and a loss of mobility. Furthermore, the herniation may create a visible bulge in the back that can be seen in an X-ray image. In some cases, this can lead to nerve compression and further complications.
Lumbar disc herniation is a painful condition in which the intervertebral disc between the lower back and the pelvis herniates, or protrudes out of its space. This can cause severe lower back pain radiating down the legs and a loss of mobility. Additionally, the herniation can be seen as a visible bulge in the back on an X-ray, creating a discomforting sight as well as physical pain.
Common symptoms of a herniated disc
If you experience any of the following symptoms, it is likely you have a herniated disc: intense pain in the middle or lower back, difficulty moving your neck or head, numbness or tingling in the arm or hand, weakness in the legs, and difficulty breathing. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible to determine the extent of the herniated disc and to discuss your treatment options.
Causes of a Herniated Disc
The most common cause of a herniated disc is a traumatic event, such as a fall. Other causes include age, obesity, and genetics. If the herniated disc is not treated, it can cause severe pain and disability.
Lifting heavy objects
There are many causes of a herniated disc, but the most common is lifting heavy objects. When the disc herniates, the nucleus pulposus (a soft, gelatinous mass) can push through the annulus fibrosis (a tough band of fibrous tissue) and into the spinal canal. This can cause extreme pain, numbness, and weakness in the lower extremities.
Poor posture
There are many causes of a herniated disc, but poor posture is a major contributor. When you sit or stand for long periods of time, your spine can become compressed, which can lead to a herniated disc. Other causes of a herniated disc include trauma, arthritis, and a tumor. If you experience pain in your back or neck, it’s important to see a doctor to determine the cause and to figure out a treatment plan.
Trauma
Herniated discs are a common cause of back pain. The disc becomes bulging and herniates through the annular ring, the tough outer ring of the disc. This can cause pressure on other surrounding discs and nerves, and can lead to pain and disability. Herniated discs are more common in the elderly, and can often be caused by a fall, a car accident, or a viral infection. Treatment includes surgery to remove the herniated disc and replace it with a new one.
Herniated Disc Treatment
There are a variety of treatment options available for a herniated disc, depending on the severity of the condition. For mild cases of herniated discs, rest and ice therapy may be sufficient. However, if the herniated disc is more severe, surgery may be necessary to remove the disc and alleviate the symptoms.
Non-surgical treatments for herniated disc
There are a number of non-surgical treatments for herniated discs. These treatments may include:
Stretching exercises for herniated disc
- There is a variety of stretching exercises that can be done to help relieve pressure on a herniated disc. One simple exercise is to lie down on your back with your knees bent and your feet flat on the ground.
- Place your hands on your lower back and slowly push your hips up until your thighs are parallel to the ground. Hold the position for a few seconds, then slowly lower your hips back to the starting position.
- Another exercise is to lie down on your back with your legs bent and your feet flat on the ground. Place your hands on your lower back and slowly push your hips up until your thighs are parallel to the ground. Hold the position for a few seconds, then slowly lower your hips back to the starting position.
Heat therapy
There is a lot of debate on the best way to treat a herniated disc. Some people believe that heat therapy is the best treatment, while others believe that surgery is the best option.
There are a few different types of heat therapy that are used to treat herniated discs. The most common type is thermal therapy, which uses heat to help break up the scar tissue that is around the herniated disc. Other types of heat therapy include electromagnetic therapy and ultrasound therapy.
Ice therapy
There is mounting evidence that ice therapy may be an effective treatment for herniated discs. A study published in the journal Spine in 2009 found that patients who received ice therapy for six weeks had a significant reduction in pain and improvement in function compared to those who received a sham treatment. In a study published in the journal Spine in 2010, researchers found that ice therapy was as effective as surgery in relieving pain and improving function in patients with herniated discs.
The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons has stated that ice therapy is an effective treatment for herniated discs and should be considered as an option for patients who do not respond to other treatments.
Taping for herniated disc
Herniated discs are a common problem, and can often be treated with surgery. However, there are other options, such as taping. Taping can help to support the disc and keep it from herniating further.
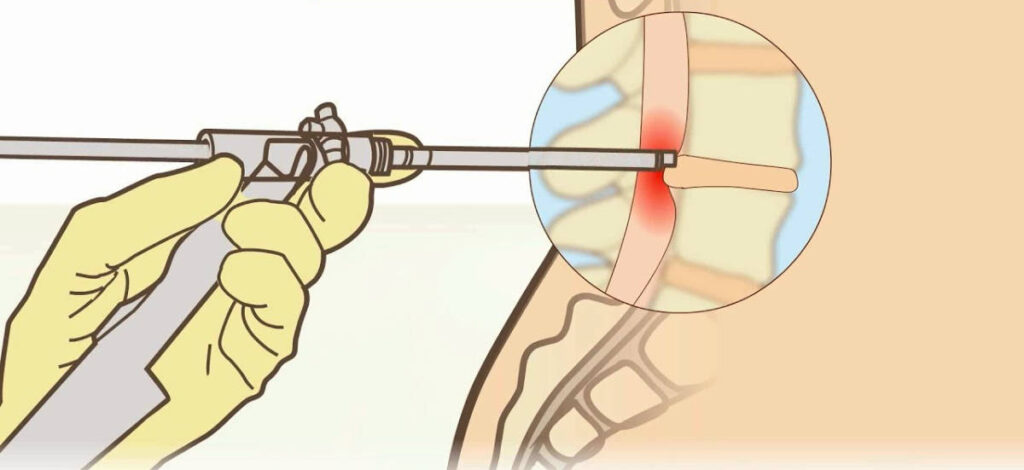
Percutaneous transluminal decompression
Herniated discs are a common cause of back pain. If the herniated disc is pressing on a nerve, the pain can be severe. Percutaneous transluminal decompression (PTC) is a procedure used to relieve the pressure on the nerve. PTC is performed by inserting a thin, metal tube through the skin and into the herniated disc. The tube is then used to press the herniated disc back into its normal position. PTC is usually successful in relieving the pain and restoring function to the affected nerve.
Each of these treatments has its own benefits and drawbacks. Some treatments may be more effective for certain types of herniated discs, while others may have more severe side effects. It is important to discuss the options available to you with a doctor before making a decision.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy can help people with herniated discs recover from the pain and disability they experience. Physical therapy may help to reduce the amount of pain a person experiences, improve range of motion, and improve strength and flexibility. Physical therapy may also help to improve the function of the spine.
Chiropractic care
Herniated discs are a common type of spinal cord compression. A herniated disc occurs when the annulus fibrosus, the tough outer layer of the disc, ruptures. The pressure from the ruptured disc can cause spinal cord compression, which can lead to nerve damage and pain.
Chiropractic care can help relieve pain and improve function by restoring the spinal cord’s normal alignment and function. Chiropractic care also helps to correct the underlying causes of spinal cord compression, such as misalignment of the spine, spinal stenosis, and herniated discs.
Pain medications
There are a variety of medications that can be used to treat herniated discs. Some of the most common pain medications used to treat herniated discs are ibuprofen and acetaminophen. Some other medications that can be used to treat herniated discs include naproxen, diclofenac, and etodolac. It is important to talk to your doctor about the best medication for you to treat your herniated disc. Also, check out this best magnesium supplement!
Surgical treatments for herniated disc
Surgical treatments for herniated disc depend on the severity of the herniated disc and the patient’s age, general health, and other medical conditions. In general, surgery is the most effective treatment for herniated discs. Surgery may include removal of the herniated disc, repair of the herniated disc, or a combination of these treatments.
If the herniated disc is small, surgery may be the only option. If the herniated disc is large, surgery may not be the only option but may be the best option. If the herniated disc is in the spinal canal, surgery may not be the only option but may be the best option.
If the herniated disc is not in the spinal canal, surgery may include removal of the herniated disc, repair of the herniated disc, or a combination of these treatments. Surgery may also include the placement of a metal plate or device to support the spine.
Microdiscectomy
Microdiscectomy is a surgical procedure used to remove a herniated portion of a disc that is causing significant pain and a limited range of motion. This procedure is often recommended when non-surgical treatments have been unsuccessful in providing relief.
Laminectomy
If you are experiencing severe back pain, you may be a good candidate for a laminectomy. A laminectomy is a surgery that removes a section of the spine. This can be done to relieve pain from a herniated disc. A herniated disc is a bulge or tear in the spinal cord that can cause severe pain. A laminectomy can also be done to remove a tumor or other mass from the spine.
How to Prevent Herniated Discs
There are a few things that you can do to help prevent herniated discs from happening. First, make sure to maintain a healthy weight. This will help to reduce the amount of pressure that is put on the discs in your back. Second, make sure to exercise regularly. This will help to keep your back flexible and strong. Finally, make sure to get regular chiropractic care. This will help to keep your back in alignment and minimize the risk of herniated discs.
Exercise regularly
If you have a herniated disc, regular exercise is essential for preventing it from worsening. Exercise can help to improve your flexibility, strength, and balance, as well as reduce the pressure on the herniated disc, thereby reducing pain and inflammation. Additionally, exercises which focus on core stability and strengthening can help to support the spine and reduce the risk of further injury.
Maintain good posture
If you are experiencing back pain, you may be wondering if you have herniated discs. A herniated disc is a soft, jelly-like mass that has slipped out of its normal position in the spine. Herniated discs can cause intense back pain, and can even lead to paralysis.
To prevent herniated discs, you should maintain good posture. Good posture means keeping your spine straight and minimizing the use of your abdominal muscles. You should also avoid activities that put a lot of stress on your back, such as heavy lifting, bending over, and sitting for long periods of time. If you do experience back pain, talk to your doctor about your options for treatment.
Practice good body mechanics
Herniated discs are a common problem that can occur in the spine. They are caused by the pressure of the spinal cord on the disc. This can cause the disc to rupture, which can cause pain and disability. To prevent this from happening, it is important to practice good body mechanics. This means keeping your spine flexible and stable and avoiding excessive pressure on your discs. You can also take supplements, such as glucosamine and chondroitin, to help support your spine. You can also read about the tips for managing joint pain!
When & How to Seek Medical Care
Fortunately, the majority of herniated discs do not require surgery and, with time, the symptoms of sciatica/radiculopathy usually improve in 9 out of 10 people. The amount of time it takes for symptoms to improve can range from a few days to a few weeks.
General Guidelines
Limit activities for 2 to 3 days, but walking should be actively encouraged as tolerated. An anti-inflammatory, such as ibuprofen, can be taken if not contraindicated for the patient. However, prolonged bed rest is not recommended and should be avoided.
Primary care evaluation during this time may lead to the consideration of other non-surgical treatments, such as physical therapy, as viable and potentially beneficial alternatives to surgery.
Radiographic imaging, such as an MRI, is not recommended by the American College of Radiology unless symptoms have been present for at least six weeks or longer.
It is advisable to get a referral to a spine expert, like a neurosurgeon if the signs continue after 4 weeks. Ahead of the consultation, a specialist may necessitate further imaging, like an MRI, to be done.
An urgent evaluation and imaging should be done if symptoms of major leg/arm weakness, loss of sensation in the genital/rectal area, lack of control of urine or stool, a past of metastatic cancer, major recent infection or fever, radiculopathy, or a fall/injury that caused the pain are present. Imaging should also be taken into consideration earlier if progressive neurologic deficit (e.g. progressive weakness) is evident on examination.
Testing & Diagnosis
Common testing modalities for this condition include MRI, plain X-rays, CT scans, myelograms, and electromyograms. MRI is the most common imaging modality and is often supplemented with plain X-rays to evaluate the affected vertebra fully. However, it should be noted that disc herniation cannot be detected on plain X-rays. CT scans and myelograms were formerly used more extensively before the introduction of MRI; however, they are now more rarely the initial diagnostic imaging, except in special cases where their use is warranted. Electromyograms are rarely employed.
- X-rays of the spine are a useful diagnostic tool that can be used to detect a variety of underlying causes of pain, such as tumors, infections, fractures, and more. By applying radiation to produce a film or picture of a part of the body, X-rays can reveal the structure of the vertebrae and the outline of the joints, providing valuable insight into potential causes of pain.
- Computed Tomography (CT or CAT) Scan is a powerful diagnostic imaging technique that uses X-rays to create detailed, cross-sectional images of the body. It provides detailed information about the shape and size of the spinal canal, its contents, and the structures around it. This imaging technique is extremely useful in helping medical professionals to diagnose and treat a variety of different medical conditions.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): A diagnostic procedure that uses powerful magnets and computer technology to generate 3D images of body structures; it can display the spinal cord, nerve roots, and their surroundings, as well as enlargements, degeneration, and tumors.
- A myelogram is an X-ray of the spinal canal after contrast material is injected into the cerebrospinal fluid. This imaging test enables clinicians to detect pressure on the spinal cord or nerves due to herniated discs, bone spurs, or tumors.
- EMG/NCS studies are used to measure the electrical impulse along nerve roots, peripheral nerves, and muscle tissue. This helps determine if there is ongoing nerve damage, healing from a past injury, or another site of nerve compression. These tests are often ordered to provide valuable insight into a patient’s neurological condition.
What is the outlook for people with herniated disks?
In most cases, herniated disk pain can be alleviated with simple medical treatment or may improve on its own over the course of a month. However, if no progress is made, it is highly recommended to visit a healthcare provider for more aggressive methods, such as injections or surgery, in order to resolve the issue.
Will a herniated disk get worse?
An untreated herniated disk can get worse, especially if you continue the activities that caused it. A worsening ruptured disk can lead to chronic (ongoing) pain and loss of control or sensation in the affected area. To avoid further complications, it is important to see your healthcare provider if symptoms persist after four to six weeks of conservative care.
Will I need to have spinal surgery?
Nine in 10 individuals with a herniated disk can find betterment with non-surgical therapies or with no therapy over time. Though, if other treatments do not bring respite, a medical care provider may suggest surgery. There are many surgical strategies on hand to ease the pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, such as:
- Diskectomy to remove your herniated disk.
- Laminectomy to remove part of the bone around a herniated disk and expand your spinal canal.
- Artificial disk surgery to replace a damaged herniated disk with an artificial one.
- Spinal fusion directly joins two or more vertebrae together to make your spine more stable.
Conclusion
It is important to remember that a herniated disc is a serious medical condition that should be treated with proper medical care. While there are many treatments available, it is important to find the one that works best for you. With the right treatment, you should be able to say goodbye to pain and discomfort and get back to living your life comfortably. If you find these blogs helpful, please share this with your loved ones and friends. You are also welcome to visit our other related blog for more tips and recommendations.