The symptoms of lupus in women, It can be hard to recognize the symptoms of Lupus in women. Lupus is an autoimmune disorder that can affect any part of the body but often has a greater impact on women. In this blog, we will discuss 15 important things that you need to know about the symptoms of Lupus in women. We will talk about the common symptoms of Lupus, the risk factors for developing Lupus, and the treatments that are available.
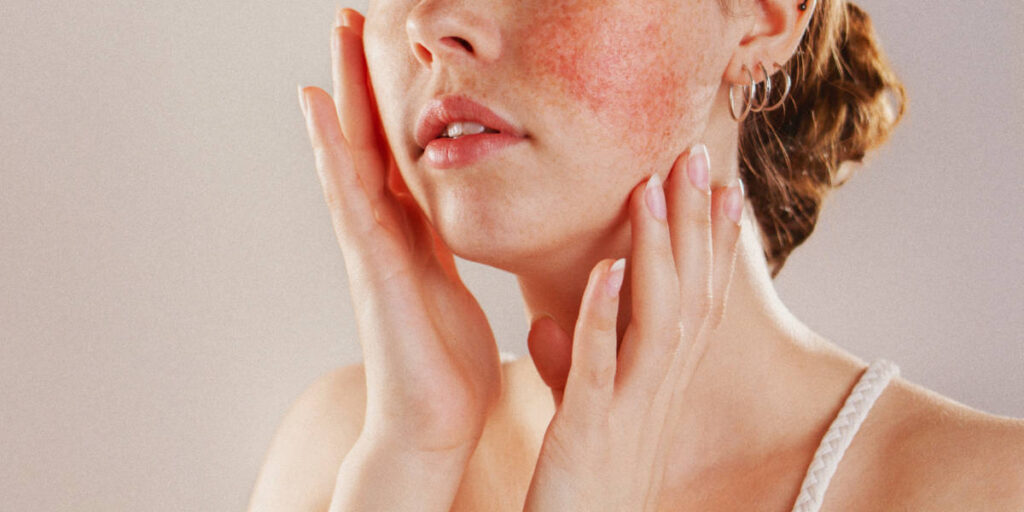

We will also discuss ways to reduce your risk of developing Lupus and tips to manage your symptoms. With this information, you can be better informed and better prepared to monitor your health.
Definition of Lupus
Lupus is a chronic, autoimmune disease caused by the body’s own immune system attacking its own tissues. Symptoms can vary widely, but most people experience some form of inflammation, pain, or swelling. Lupus can affect any part of the body but is most commonly seen in the skin, joints, and kidneys. There is no known cure for lupus, but treatments can help manage the disease and improve symptoms.
The Symptoms of Lupus in Women
The prevalence of lupus in women is unknown but is thought to be higher than in men. Lupus is most common in women between the ages of 25 and 44 years. The incidence of lupus in women is also increasing and is now more common than in men. Lupus is a serious autoimmune disorder that can affect any body part or system. The most common symptoms are skin rashes, joint pain, and fatigue. There is no known cure for lupus, but treatments can help manage the symptoms.
Signs and Symptoms of Lupus
There are many signs and symptoms of lupus, but some of the most common include fatigue, joint pain, skin rash, and kidney problems. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor to determine if you have lupus.
Common Symptoms of Lupus
Joint Pain
There is no definitive answer to the question of what causes joint pain in people with lupus. However, there are a number of factors that may contribute, including:
-Infections, such as those caused by the Epstein-Barr virus or Lyme disease
-Inflammation of the joints
-Injury to the joints
-Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Sjogren’s syndrome, can damage the cartilage and bone in the joints
-Lupus can also damage the nerves that supply the joints with information about how the joint should move
-Diseases that affect the immune system, such as HIV or cancer, can also lead to joint pain in people with lupus
There is no definitive answer to the question of what causes joint pain in people with lupus. However, there are a number of factors that may contribute, including:
-Infections, such as those caused by the Epstein-Barr virus or Lyme disease
-Inflammation of the joints
-Injury to the joints
-Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Sjogren’s syndrome, can damage the cartilage and bone in the joints
-Lupus can also damage the nerves that supply the joints with information about how the joint should move
-Diseases that affect the immune system, such as HIV or cancer, can also lead to joint pain in people with lupus.
Fatigue Cause of Lupus
There is no definitive answer as to why people develop lupus. However, researchers believe that a combination of environmental and genetic factors is involved. Some of the more commonly cited causes of lupus include:
-Genetic predisposition
-Environmental factors, such as exposure to sunlight, pollution, and viruses
-Complications from other diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or Sjogren’s syndrome
-Lack of sleep
-Psychological factors, such as stress or anxiety
Lupus can be a debilitating disease. It can cause severe pain and inflammation, as well as damage to organs such as the kidneys, lungs, and heart. In some cases, lupus can even lead to death.
There is no cure for lupus, but there are treatments that can help manage the symptoms. Most people with lupus need to take medications to control the symptoms, and often need to see a doctor regularly to check their progress.
Fever
There is no definitive answer to this question. Some people believe that lupus can be caused by a fever, while others believe that lupus cannot be caused by a fever. Some people believe that lupus can be caused by a combination of factors, including a fever. It is still unclear which, if any, of these factors is actually responsible for causing lupus.
Skin Rashes Cause of Lupus
There are many potential causes of skin rashes, including lupus. Lupus can cause skin rashes due to inflammation and irritation of the skin, as well as damage to the skin. Symptoms of lupus-related skin rashes can include redness, swelling, itching, pain, and changes in skin texture or color. It is important to note that not all rashes are caused by lupus, so it is essential to seek medical advice in order to correctly diagnose any potential skin condition.
Other Symptoms of Lupus
Muscular Pain Cause of Lupus
There is no single definitive answer to this question, as the cause of muscular pain can vary greatly from person to person with lupus. However, some of the most common causes of muscular pain in individuals with lupus include inflammation of the muscles, joint pain, stress and lack of exercise, medication side effects, and infection. Additionally, some lupus-related conditions such as fibromyalgia and vasculitis can also contribute to muscular pain. Treatment for muscular pain often involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, and medications. It is important to speak with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for managing muscular pain.
• Muscle stiffness
• Muscle pain
• Muscle spasms
• Muscle fatigue
• Muscle weakness
• Muscle inflammation
• Muscle degeneration
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult your doctor to determine the cause and to determine if there is a treatment option available.
Hair Loss Cause of Lupus
There is no definitive answer to the question of what causes hair loss in people with lupus. However, some potential causes include:
-Medications: Some medications can cause hair loss, including corticosteroids and antibiotics.
-Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes, such as during menopause, can lead to hair loss.
-Autoimmune disease: Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus, can cause hair loss as a result of the body’s immune system attacking the hair follicles.
-Treatment: Hair loss can also be a result of treatment for lupus, such as corticosteroids or chemotherapy.
Swelling in the Hands, Feet, and other Areas
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can cause swelling in the hands, feet, and other areas. Swelling can be a sign of an underlying condition, such as an infection, and requires prompt treatment. If left untreated, swelling can lead to other complications, such as ulcers and gangrene.
Raynaud’s Phenomenon
Raynaud’s Phenomenon is a disorder that can be associated with lupus. It is characterized by reduced blood flow to the hands, feet, and other extremities, resulting in pain, redness, and even frostbite. This reduced blood flow is caused by a decrease in the diameter of the small arteries, leading to decreased circulation in the affected areas. Treatment options for this condition include lifestyle modifications, medications, and, in some cases, surgery.
Diagnosing Lupus Cause of Lupus
There is no definitive test that can determine the cause of lupus, but a variety of tests and procedures may be used to rule out other possible causes. Blood tests that measure the levels of certain proteins and antibodies may be used to determine if the person has an autoimmune disease. Imaging tests, such as x-rays or CT scans, may be used to determine if the person has a lesion or tumor on their body.
Lupus can be difficult to diagnose, and it may take several tests and examinations to determine the cause of the person’s lupus. If the person has lupus, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible to determine the best course of treatment.
Tests Used to Diagnose Lupus
The most common tests used to diagnose lupus are the blood tests, which look for the presence of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) and other markers of the disease. Other tests that may be used to help determine the cause of lupus include:
1. A complete blood count (CBC) to measure the number and types of white blood cells in the blood.
2. A serum Lupus Anticoagulant (Lupus Anticoagulant Screen) test to measure the level of a protein that can increase the risk of blood clots.
3. A T-cell immunophenotype test to look for specific changes in the number, function, and shape of T cells.
4. A urinalysis to check for the presence of protein in the urine.
5. An electrocardiogram (EKG) is to look for changes in the electrical activity of the heart.
Other Considerations
There are many potential causes of lupus, but the most common are unknown. Some people are born with the disease, while others develop it after a viral or other infection. Some people inherit a gene that causes lupus, while others develop lupus after experiencing a traumatic event.
Some people believe that lupus is caused by a combination of environmental and genetic factors. Lupus is more common in women than in men, and it tends to run in families. Some people with lupus develop a severe form of the disease, while others have milder lupus.
There is no known cure for lupus, but treatments can help improve the symptoms of the disease. Some people require long-term treatment, while others only require short-term treatment. Treatment options include medications, surgery, and radiation therapy.
People with lupus should always consult with their doctor to determine the best treatment option for them.
Treating Lupus
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to treating lupus, as the disease is highly individualized. Treatment typically focuses on managing the symptoms of the disease and preventing additional damage. Treatment options may include medications, therapy, and surgery.
Some people may need to take multiple medications to control their symptoms. Other people may only need to take one medication. Some people may need to see a doctor or therapist regularly, while others may only need to see them once or twice a year. Some people may need to have surgery, while others may only need to take medications.
Each person with lupus is unique, and there is no one treatment that is guaranteed to work for everyone. It is important to work with a doctor or therapist who is familiar with lupus to find the best treatment for you.
Medications
There is no one cause of lupus, but medications can play a role. Some medications are known to cause lupus, while others may increase your risk if you have the disease.
Some medications that have been linked to lupus include:
-Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn)
-Birth control pills
-Hormone replacement therapy
-Some cancer medications
-Some psychiatric medications
If you are taking any of these medications and develop lupus, your doctor may want to change your medication or stop it altogether.
Other Treatment Options Cause of Lupus
There are a variety of treatments for lupus, and each person’s treatment plan depends on the specific symptoms and features of the disease. Some common treatments include:
-Medications to help reduce the symptoms of lupus, such as corticosteroids and immunosuppressants
-Surgery to correct the underlying cause of lupus, such as a hernia or a tumor
-Plastic surgery to improve the appearance of the skin
-Alternative medicine, such as acupuncture or massage
-Home remedies, such as garlic or fish oil supplements
Some people find that a combination of treatments is best for them. The goal of treatment is to help the person with lupus feel better and live a normal life as possible. You can also read about how to increase vitality!
Self-Care Tips for Women Living With Lupus
There are many ways to care for yourself while living with lupus. Below are some self-care tips to help you feel better:
1. Get enough sleep. Sleep is essential for your overall health and well-being, and it’s especially important for people with lupus. Try to get at least seven hours of sleep each night.
2. Eat a balanced diet. Eat foods that are high in antioxidants and low in inflammation-causing foods.
3. Exercise. Exercise can help improve your mood and reduce your symptoms. Try to get at least 30 minutes of exercise each day.
4. Get massages and acupuncture. Massages and acupuncture can help reduce pain and inflammation.
5. Take medications as prescribed. Take the medications your doctor prescribes to reduce your symptoms.
Stress Management Living With Lupus
Stress management is something that everyone needs to take into account when living with lupus. It is important to have a plan in place to deal with stress and to stick to it. There are a few things that you can do to help manage your stress:
1. Make a list of your priorities. What are the things that are most important to you? What are the things that you need to focus on to maintain your quality of life? Once you have a list, make sure to stick to it.
2. Take care of yourself. Eat healthy, get enough sleep, and exercise. These things will help to improve your overall health and well-being.
3. Connect with others. It is important to have a support system, and people who understand what you are going through. Connect with your friends and family, and let them know how you are doing.
4. Take care of your emotions. When you are feeling stressed, it is easy to let your emotions get the best of you. Don’t let yourself get caught up in negative thoughts and feelings. Instead, take some time to calm down and relax.
5. Don’t bottle up your stress. If you are feeling overwhelmed, it is important to let out your feelings. Talk to your friends, family, or therapist about what is going on. It can be helpful to get your feelings out in a safe and healthy way.
Regular Exercise Living With Lupus
Regular exercise has been shown to be beneficial for people living with lupus. It has been shown to help improve the overall quality of life, reduce symptoms, and help manage the disease. Exercise can also help improve mood and energy levels.
There are a few things to keep in mind when starting an exercise program for people living with lupus. First, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to make sure that the exercise is appropriate for your individual situation. Second, it is important to be aware of the risks and precautions associated with exercise. Third, be sure to drink plenty of fluids before, during, and after exercise to avoid dehydration. And finally, be sure to take breaks often and allow your body to rest.
Healthy Diet
If you are living with lupus, it is important to maintain a healthy diet. Eating a balanced and healthy diet will help to keep your lupus in check, as well as help prevent other health problems. Some good foods to include in your diet if you have lupus include:
-Fruits and vegetables: Eat plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables to help boost your overall health and keep your lupus in check.
-Lean protein: Include lean protein in your meals to help keep your energy levels up and to help build muscle.
-Low-fat dairy: Include low-fat dairy in your diet to help boost your calcium intake and to help reduce the risk of heart disease.
-Whole grains: Include whole grains in your diet to help improve your digestion and to help reduce the risk of heart disease.
Proper Sleep
Proper sleep is essential for living with lupus. Lack of sleep can worsen lupus symptoms and increase the risk of developing other medical conditions.
People with lupus should get at least 7 to 8 hours of sleep each night. However, because lupus can cause sleep disturbances, it is important for people with lupus to talk with their doctor about the best way to get the sleep they need. Some people may need to take medication to help them sleep. Others may need to adjust their sleep schedule or live in a quiet environment to get the sleep they need.
There are many ways to get the sleep you need. Some people may need to adjust their sleep schedule or live in a quiet environment to get the sleep they need. Others may need to take medication to help them sleep.
Conclusion
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect women of any age, race, or ethnicity. While the cause of lupus is unknown, its symptoms can range from mild to severe and can have a significant impact on women’s lives. It is important to be aware of the different signs and symptoms of lupus in order to seek prompt medical attention.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help to manage the condition and improve the quality of life of those with lupus. When it comes to managing lupus, it is important to stay informed and work closely with healthcare providers. By being proactive and taking control of your health, you can live a healthier and fuller life. If you find these blogs helpful, please share this with your loved ones and friends. You are also welcome to visit our other related blog for more tips and recommendations.